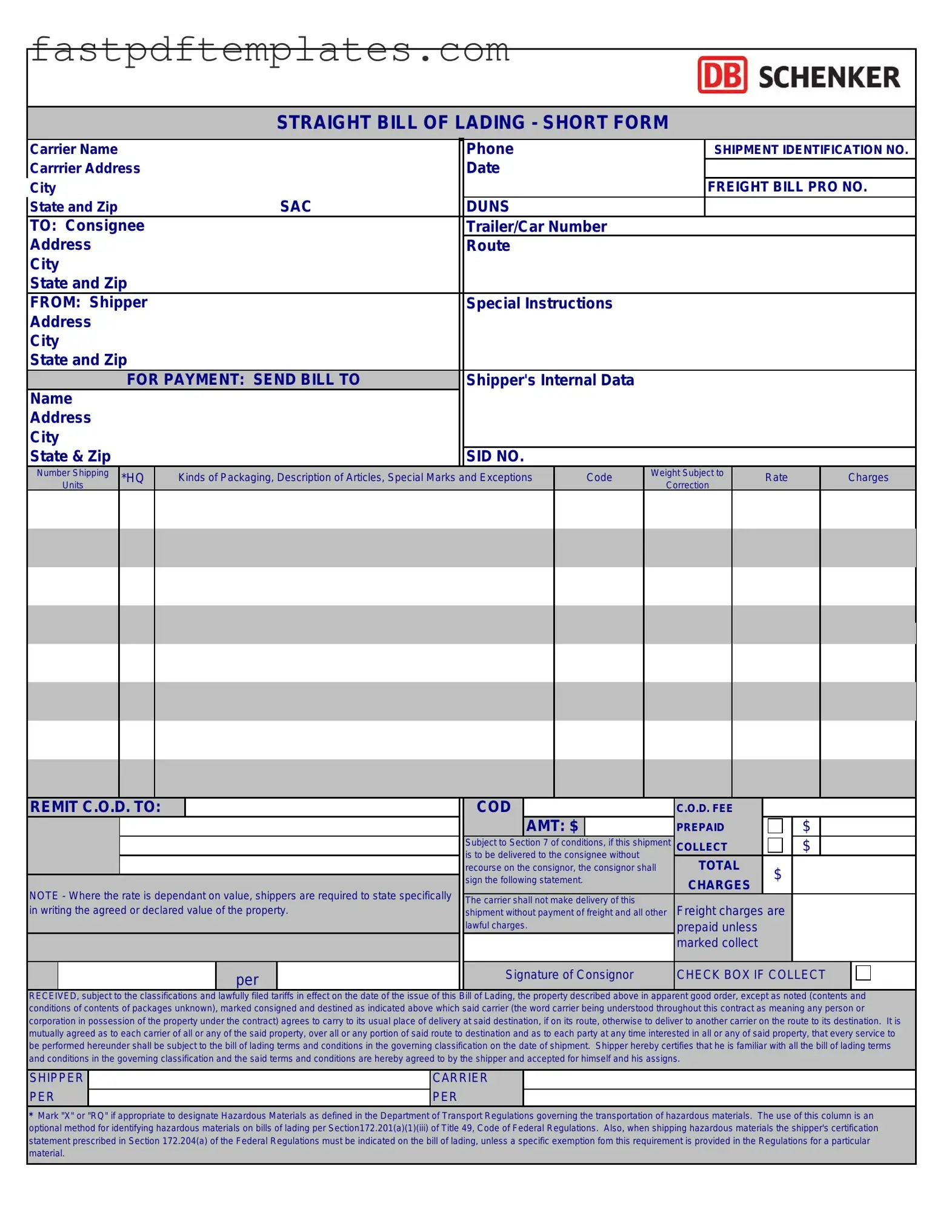
The Straight Bill of Lading is similar to the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) form. Both documents serve as evidence of a contract for the sale of goods. They outline the terms of shipment and delivery, providing a clear record that helps protect the rights of both the buyer and the seller. The UCC also provides guidelines for the transfer of ownership, much like how a Straight Bill of Lading indicates the transfer of goods from the shipper to the consignee.
Another document that shares similarities is the Order Bill of Lading. While the Straight Bill of Lading is non-negotiable, the Order Bill can be transferred to others. Both documents serve the same purpose of facilitating the shipment of goods, but the Order Bill allows for greater flexibility in transferring ownership during transit. This can be particularly useful in commercial transactions where goods might change hands multiple times.
The Freight Bill is another related document. It details the charges for transporting goods and is usually issued by the carrier. While the Straight Bill of Lading focuses on the shipment itself, the Freight Bill emphasizes the cost aspect. Both documents work together to ensure that all parties understand their obligations regarding payment and delivery.
The Warehouse Receipt also bears similarities to the Straight Bill of Lading. A Warehouse Receipt serves as proof of storage and ownership of goods held in a warehouse. Like the Straight Bill, it outlines the specifics of the goods, including quantity and condition. Both documents provide evidence of ownership and can be used in transactions involving the sale or transfer of goods.
Next, the Shipping Receipt is comparable to the Straight Bill of Lading in that it confirms the receipt of goods by the carrier. This document often includes details about the shipment, similar to those found in a Straight Bill. Both documents serve as proof that the goods were handed over to the carrier for transport.
The Commercial Invoice is another document that aligns closely with the Straight Bill of Lading. This invoice details the transaction between the buyer and seller, including descriptions of the goods, quantities, and prices. While the Straight Bill focuses on the transportation aspect, the Commercial Invoice provides a financial overview of the transaction, ensuring clarity for all parties involved.
The Export Declaration is also similar, especially in international shipping contexts. This document is required for goods leaving the country and provides information about the shipment. Like the Straight Bill of Lading, it ensures that all parties are aware of what is being shipped and under what terms, helping to facilitate smoother customs processes.
The Packing List is another document that complements the Straight Bill of Lading. It details the contents of a shipment, including item descriptions and quantities. While the Straight Bill serves as a contract for transport, the Packing List provides a breakdown of what is included, ensuring that the consignee receives exactly what was shipped.
The Consignment Note is also akin to the Straight Bill of Lading. This document serves as a record of the goods sent to a consignee. It includes information about the sender, recipient, and shipment details. Both documents serve as important records that help track and confirm the movement of goods.
Finally, the Delivery Order is similar in that it instructs the carrier to release goods to the consignee. While the Straight Bill of Lading acts as a contract for the shipment, the Delivery Order facilitates the actual transfer of goods. Both documents work together to ensure that the consignee receives the correct items in a timely manner.