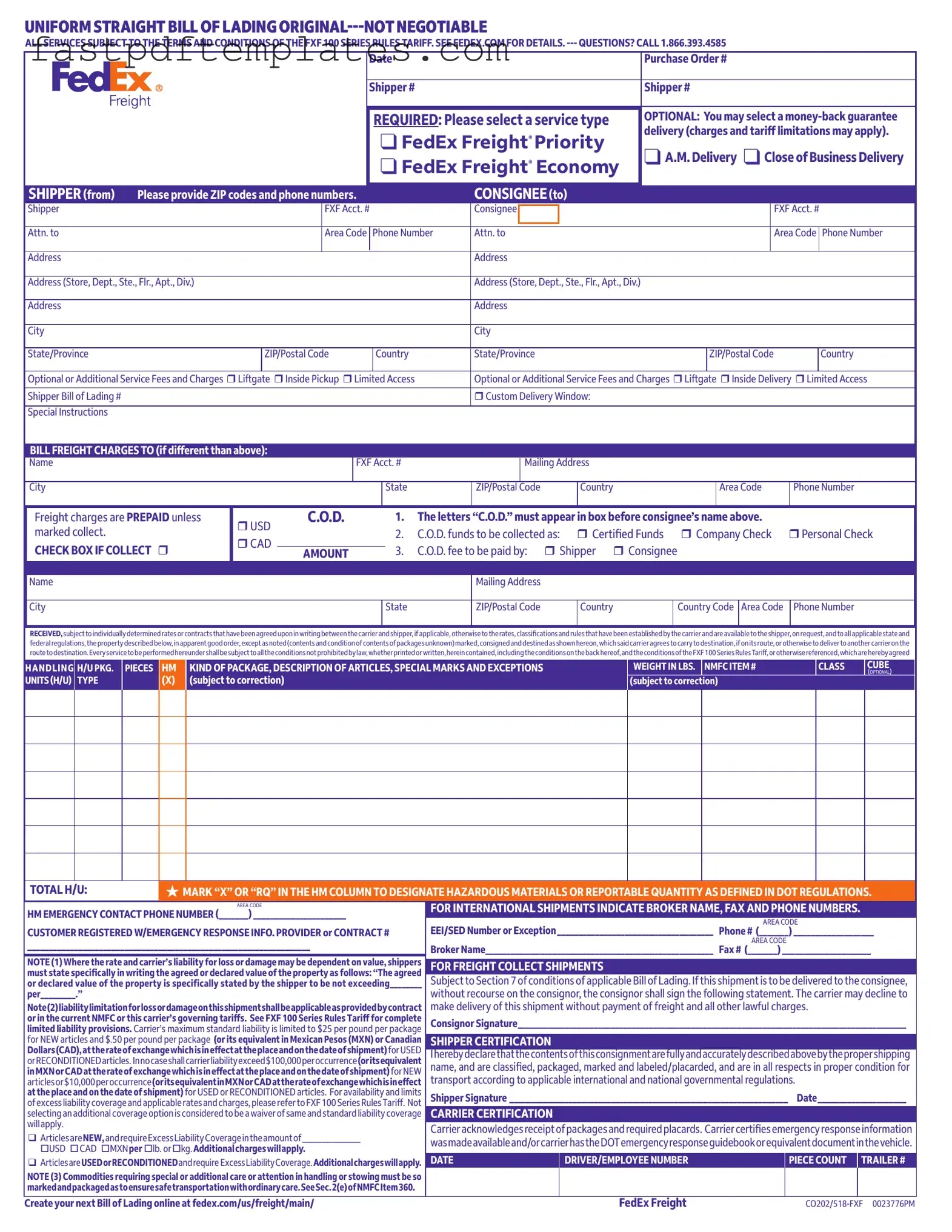
The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) Bill of Lading is a document that serves a similar purpose to the FedEx Bill of Lading. Like the FedEx form, it acts as a contract between the shipper and the carrier, detailing the terms of the shipment. It includes information about the goods being transported, the parties involved, and the shipping terms. The UCC Bill of Lading is often used in domestic freight transactions, ensuring that both parties understand their rights and responsibilities. Additionally, it can be negotiable or non-negotiable, providing flexibility in how the goods are handled during transit.
The Air Waybill (AWB) is another document closely related to the FedEx Bill of Lading. This document is specifically used for air freight shipments. Similar to the FedEx form, the AWB serves as a contract between the shipper and the airline, outlining the details of the shipment, including the nature of the goods and the destination. The AWB also acts as a receipt for the goods, confirming that the airline has taken possession of the cargo. Unlike the FedEx Bill of Lading, the AWB is typically non-negotiable, meaning it cannot be transferred to another party.
The Ocean Bill of Lading is a maritime equivalent to the FedEx Bill of Lading. Used in shipping goods by sea, this document serves both as a contract and a receipt for the goods. It contains detailed information about the shipment, including the type of cargo, the shipping route, and the terms of transport. The Ocean Bill of Lading can be negotiable, allowing the shipper to transfer ownership of the goods while in transit. Like the FedEx form, it provides legal protection for both the shipper and the carrier.
The Consignment Note is similar to the FedEx Bill of Lading in that it documents the agreement between the sender and the carrier. This document is often used in less-than-truckload (LTL) shipments. It includes essential details about the shipment, such as the sender's and receiver's information, a description of the goods, and any special handling instructions. While it serves a similar purpose, the Consignment Note is generally less formal than the FedEx Bill of Lading and may not carry the same legal weight in some jurisdictions.
The Delivery Order is another document that shares similarities with the FedEx Bill of Lading. This document is issued by the carrier, instructing the delivery of goods to a specific party. It serves as a release order, allowing the consignee to take possession of the cargo. While the FedEx Bill of Lading acts as a contract for the transportation of goods, the Delivery Order is primarily concerned with the final delivery process. Both documents are essential in ensuring that the right parties receive the correct shipments.
The Freight Invoice is a financial document that accompanies the FedEx Bill of Lading. While the Bill of Lading outlines the terms of shipment, the Freight Invoice details the charges associated with that shipment. It includes information such as shipping costs, additional fees, and payment terms. Both documents work together to ensure transparency in the shipping process, allowing shippers and consignees to understand the financial obligations related to their shipment.
Finally, the Packing List is a document that complements the FedEx Bill of Lading by providing a detailed account of the items included in the shipment. It lists each item, its quantity, and any relevant descriptions. While the Bill of Lading serves as a contract and receipt for the shipment, the Packing List aids in inventory management and ensures that the consignee receives all items as expected. Both documents play crucial roles in the shipping process, facilitating smooth transactions and minimizing disputes.